Managing Risks of Plant
What is Plant?
Plant includes machinery, equipment, appliances, containers, implements and tools, and any component or fitting.
Construction Plant Examples:
- Mobile plant: Excavators, loaders, forklifts, trucks, cranes, elevated work platforms (EWP)
- Fixed plant: Concrete pumps, compressors, generators, scaffolding
- Power tools: Saws, grinders, drills, nail guns, welding equipment
- Pressure equipment: Air compressors, pressure vessels
- Lifting equipment: Cranes, hoists, lifting beams, slings
Common Plant Hazards
Mechanical hazards:
- Crush points, shear points, entanglement
- Ejected parts or materials
- Moving parts (blades, gears, belts, chains)
Non-mechanical hazards:
- Electricity
- Noise and vibration
- Heat, fire, explosion
- Hazardous substances (fumes, dust, hydraulic fluids)
Operational hazards:
- Rollover or tip-over
- Collision with workers, structures, other plant
- Falls from height (working on/near plant)
- Loads falling from height
Who Has Duties?
PCBUs
Must:
- Manage plant risks through risk management process
- Ensure plant safe for intended use
- Maintain plant in safe condition
- Provide information, training, supervision
- Ensure operators licensed/competent
- Register certain high-risk plant
Designers, Manufacturers, Suppliers, Installers
Must:
- Ensure plant designed, manufactured, supplied, installed without risks
- Provide safety information
- Test and commission before supply
High-Risk Work Licences
WHS Regulation requires licences for:
- Cranes: Bridge/gantry, derrick, portal boom, tower, vehicle loading
- Hoists: Materials hoists, personnel/materials hoists
- Forklifts: All classes
- Elevating work platforms (EWP): Boom-type (boom length of 11 metres or more)
- Rigging: Basic, intermediate, advanced
- Dogging: Directing crane operations, slinging loads
- Scaffolding: Basic, intermediate, advanced
- Pressure equipment: Boilers, turbines (in some jurisdictions)
Always verify operator licences before allowing operation. Licences available at Industrial Relations NSW
Risk Management for Plant
1. Identify Hazards
Throughout Plant Lifecycle:
- Design: Inherent hazards in design
- Purchase: Suitability for intended use
- Installation: Commissioning, structural support
- Operation: Normal use hazards
- Maintenance: Access, isolation, stored energy
- Decommissioning: Safe dismantling and disposal
2. Assess Risks
Consider:
- Potential injuries (severity and likelihood)
- Who is at risk (operators, other workers, public)
- When risks arise (operation, maintenance, emergencies)
- Existing control measures
3. Control Risks: Hierarchy of Control
Level 1: Elimination
- Eliminate need for plant
- Example: Pre-cast panels eliminate on-site formwork systems
Level 2: Substitution/Engineering
Purchase Safe Plant:
- Select plant with built-in safety features
- Example: Excavator with ROPS (rollover protective structure), proximity detection systems
Guarding:
- Fixed guards (permanent barriers over dangerous parts)
- Interlocked guards (machine stops when guard opened)
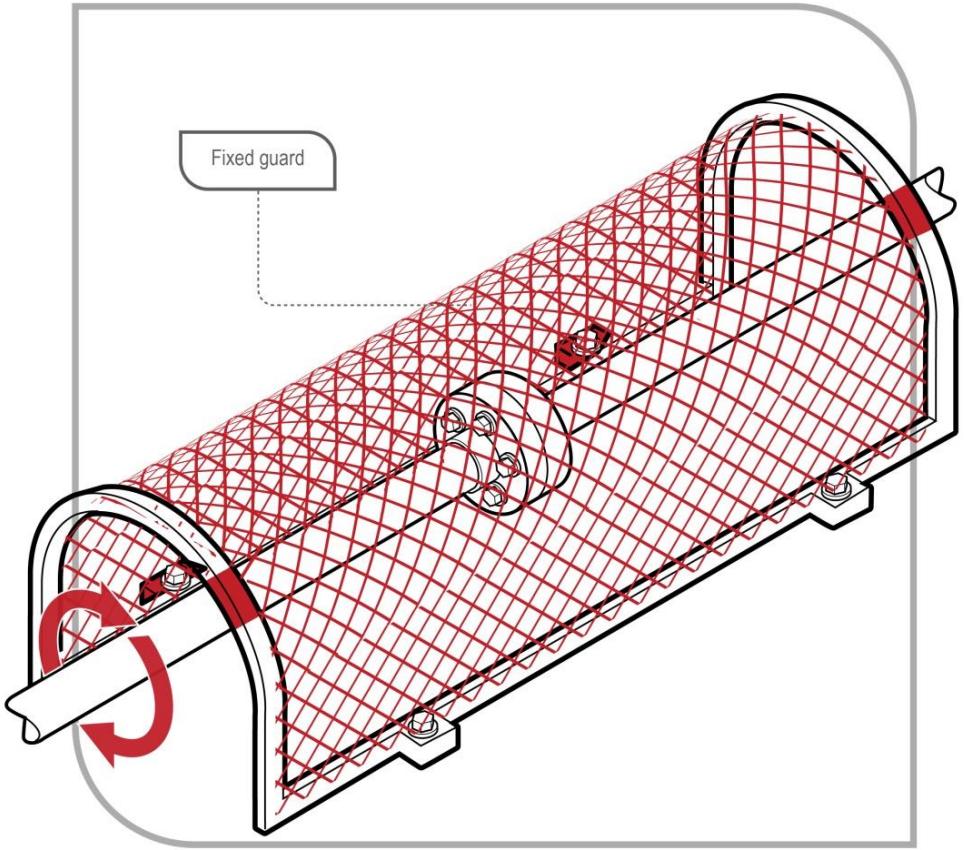 Figure: Fixed guard preventing access to rotating shaft
Figure: Fixed guard preventing access to rotating shaft
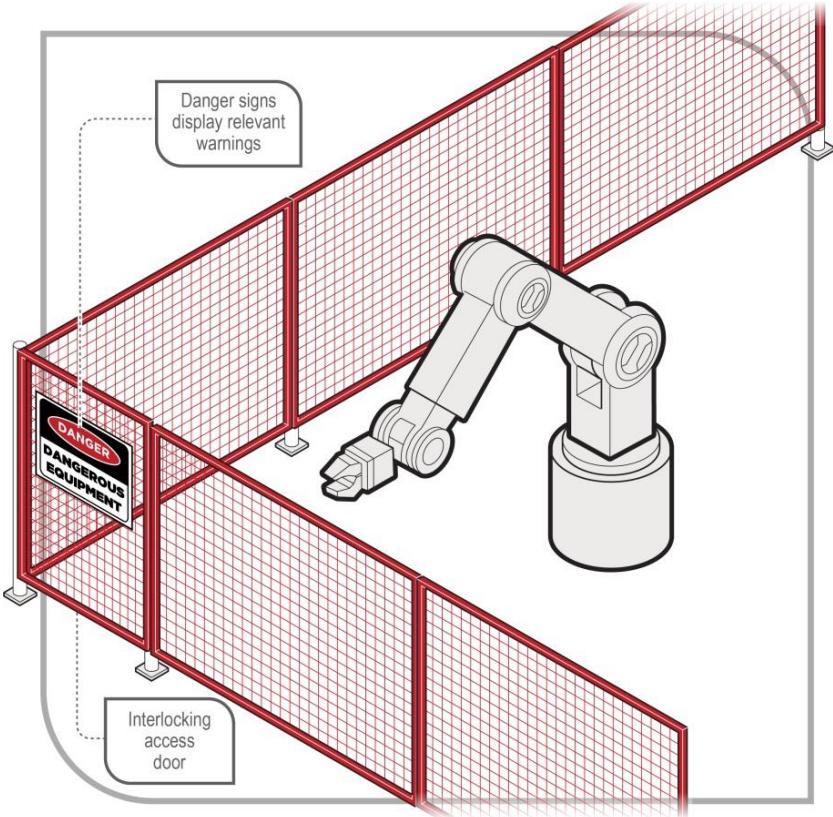 Figure: Perimeter fence guard with fixed panels and interlocking access door
Figure: Perimeter fence guard with fixed panels and interlocking access door
- Adjustable guards (for different operations)
Example: Circular saw with retractable blade guard.
Operational Controls:
- Two-hand controls (both hands required, keeps hands away from danger zone)
- Hold-to-run controls (requires continuous activation)
- Proximity sensors (detects workers, stops machine)
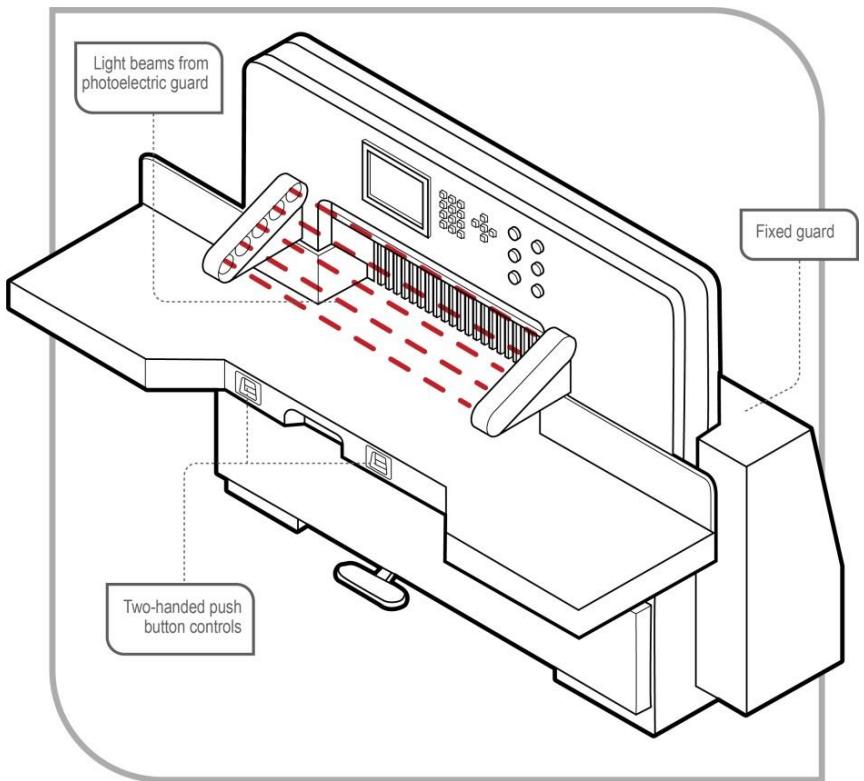 Figure: Light curtain presence sensing system
Figure: Light curtain presence sensing system
- Speed limiters, load limiters
Emergency Stops:
- Readily accessible
- Clearly identified (red mushroom button)
- Stops machine immediately
 Figure: Typical emergency stop button
Figure: Typical emergency stop button
Isolation:
- Lockout/tagout for maintenance
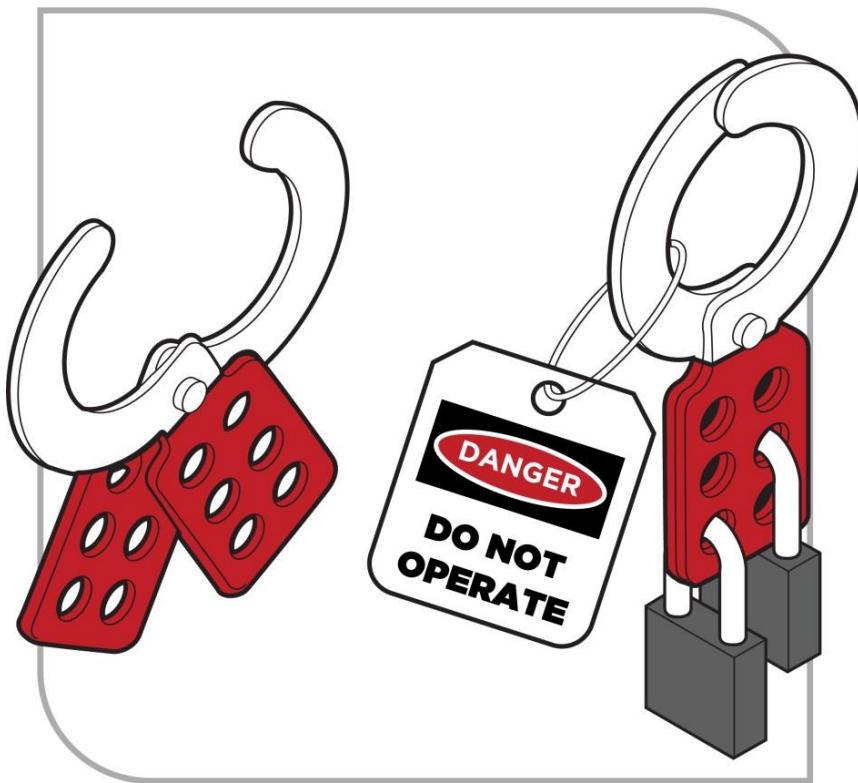 Figure: Example of lock-out with tag and multiple padlocks
Figure: Example of lock-out with tag and multiple padlocks
- Isolation of electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical energy
- Dissipation of stored energy (springs, pressure, suspended loads)
Level 3: Administrative/PPE
- Safe work procedures
- Training and competency assessment
- Permits for high-risk plant operations
- Exclusion zones around operating plant
- Pre-start inspections
- PPE (hearing protection, hi-vis, hard hats, safety boots)
4. Maintain and Review
- Regular inspections (daily pre-start, periodic detailed)
- Preventive maintenance schedules
- Competent person conducts maintenance
- Record keeping
- Review after incidents or near-misses
Mobile Plant Safety
Separation of Vehicles and Pedestrians
Principle: Keep people and moving vehicles apart.
Controls:
- Dedicated pedestrian walkways (physically separated)
- Exclusion zones (barricades, signage)
- Traffic management plan
- Designated crossing points
- Spotters for reversing/confined areas
Example: Fenced walkways on construction site separate workers from vehicle routes.
Proximity Detection Systems
- Sensors detect workers near plant
- Alerts operator (visual/audible warning)
- May automatically stop or slow plant
- Useful for excavators, trucks with blind spots
Visibility
- Reversing cameras and monitors
- Mirrors and visibility aids
- High-visibility clothing for workers
- Flashing beacons on plant
- Reversing alarms
Reversing causes many injuries/fatalities. Eliminate reversing where possible, use spotters where unavoidable.
Rollover and Tip-Over Protection
- ROPS (rollover protective structures)
- Seatbelts (must be worn in ROPS-equipped plant)
- Operating within load ratings and stability limits
- Level, stable ground conditions
- Avoid slopes, edges, underground voids
Quad Bikes:
- From 11 October 2021, all new and imported second-hand general use quad bikes must be fitted with an operator protective device (OPD) to protect riders in the event of a rollover.
Lifting Operations
Before Lifting
- Plan the lift (load weight, lift path, hazards, exclusion zone)
- Select appropriate equipment (crane capacity, rigging)
- Inspect lifting equipment (cranes, slings, shackles)
- Brief all involved (crane operator, dogger, rigger, workers)
- Establish exclusion zone (no workers under suspended loads)
During Lifting
- Competent dogger directs crane operator
- Clear communication (hand signals, radio)
- Lift smoothly (no jerking or swinging)
- No workers under suspended load
- Secure load against wind, movement
Rigging and Slinging
- Calculate load weight
- Select correct slings (capacity, condition)
- Inspect slings before use (cuts, wear, damage)
- Use correct hitches and fittings
- Ensure load balanced and secure
Elevated Work Platforms (EWP)
Types:
- Scissor lifts (vertical)
- Boom lifts (articulated/telescopic)
- Mobile and stationary
Safety Requirements:
- Licensed operators (boom-type >11m vertical)
- Pre-start inspection
- Level, stable ground (use outriggers if fitted)
- Guardrails intact on platform
- Harnesses required for boom-type (anchor to platform)
- Avoid overhead hazards (powerlines, structures)
- Do not exceed platform load rating
- Lower platform when traveling
Maintain safe distances from powerlines. De-energize lines or use insulated/non-conductive equipment where work near powerlines unavoidable.
Scaffolding
Licensing:
- Basic scaffold licence: Scaffolds up to 4 meters
- Intermediate scaffold licence: All scaffolds
- Advanced scaffold licence: Design and inspection of scaffolds
Safety Requirements:
- Designed for loads (live load, wind load, materials storage)
- Erected by licensed scaffolder
- Inspected before use and regularly
- Tagged (green tag = safe to use, red tag = unsafe)
- Edge protection (toe boards, mid-rails, handrails)
- Safe access (ladders, stairs)
- Stable foundation (base plates, mud sills)
- Tied to structure (prevent movement/collapse)
See Construction Work for detailed scaffolding guidance.
Plant Registration
Certain high-risk plant must be registered:
- Cranes (various types)
- Hoists
- Pressure vessels and boilers
- Gas cylinders
Purpose: Ensures design verified, item inspected, safe to operate.
Inspections and Maintenance
Pre-Start Inspections (Daily)
Operator checks:
- Damage, leaks, loose parts
- Safety devices functioning (guards, emergency stops, alarms)
- Fluid levels, tire pressures
- Lights, indicators, controls
Record findings, report defects, do not use defective plant.
Periodic Inspections
Competent person conducts detailed inspections at intervals based on:
- Manufacturer recommendations
- Regulatory requirements (e.g., cranes, hoists)
- Risk assessment
Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer maintenance schedules
- Use qualified technicians
- Keep records (maintenance log)
- Ensure isolated before maintenance
- Test after repairs before returning to service
Practical Construction Example
Scenario: Using 20-tonne excavator for bulk excavation
Hazards Identified
- Rollover on sloped ground
- Striking workers or other plant
- Contact with underground services (gas, electricity)
- Noise and vibration
Controls Implemented
Engineering:
- Excavator equipped with ROPS and seatbelt
- Proximity detection sensors installed
- Reversing camera and alarm
Administrative:
- Licensed operator (verified before operation)
- Service location completed (Dial Before You Dig)
- Services marked on ground
- Exclusion zone 5 meters around excavator (barricades, signage)
- Traffic management plan (separate vehicle and pedestrian routes)
- Pre-start inspection completed and recorded
PPE (for nearby workers):
- Hard hats, hi-vis, safety boots, hearing protection
Maintenance
- Daily pre-start checks
- 250-hour service completed (recorded in log)
- Hydraulic hoses inspected (no leaks or damage)