Managing Risk of Falls at Workplaces
Falls from Height - Major Hazard
Falls from height are the leading cause of death and serious injury in construction.
Common Fall Scenarios:
- Falling from roofs, edges of floors/slabs
- Through fragile surfaces (skylight, roof sheets)
- From ladders, scaffolding, elevated work platforms
- Into excavations or voids
- From structures during erection/demolition
Falls from even low heights (< 2 meters) can cause serious injury or death, especially if landing on hard surfaces or striking objects.
When is Work at Height High-Risk Construction Work?
Work involving risk of fall > 2 meters requires Safe Work Method Statement.
Examples:
- Roof work on houses (typically 3-4m from ground)
- Working on slabs/floors of multi-storey buildings
- Scaffolding erection/use
- Working from ladders >2m
Who Has Duties?
PCBUs
Must:
- Eliminate risks of falls (where reasonably practicable)
- If not practicable to eliminate, minimize risks
- Provide fall protection systems
- Ensure workers trained in fall protection use
- Prepare SWMS for work >2m fall risk
Designers
Must design structures to:
- Eliminate or minimize fall risks during construction, use, maintenance, demolition
- Include permanent anchorage points for maintenance access
- Provide safe access for ongoing maintenance
Workers
Must:
- Follow safe work procedures and SWMS
- Use fall protection equipment as instructed
- Report damaged or defective equipment
- Not remove or bypass safety systems
Hierarchy of Control for Falls
Level 1: Elimination
Most Effective: Remove the need to work at height.
Methods:
- Pre-fabricate at ground level, lift into position
- Design roof trusses on ground, crane to roof
- Use tilt-up construction (walls erected from ground)
- Remote inspection (drones, cameras) instead of physical access
Example: Pre-fabricate roof sections complete with battens and flashing on ground. Crane to roof as complete units, eliminating most work at heights.
Level 2: Minimize Risk - Passive Fall Prevention
If elimination not practicable, prevent falls using passive systems (physical barriers).
Guardrails/Edge Protection:
- Top rail at 900-1100mm
- Mid-rail
- Toe board (minimum 100mm)
- Strong enough to withstand leaning/impact
- No gaps > 250mm
Advantages:
- Protects everyone in area (not just those wearing harnesses)
- No special training required
- Does not rely on worker behavior
- Most reliable control
Applications:
- Slab edges during construction
- Roof edges
- Scaffold platforms
- Mezzanine floors
- Stair openings
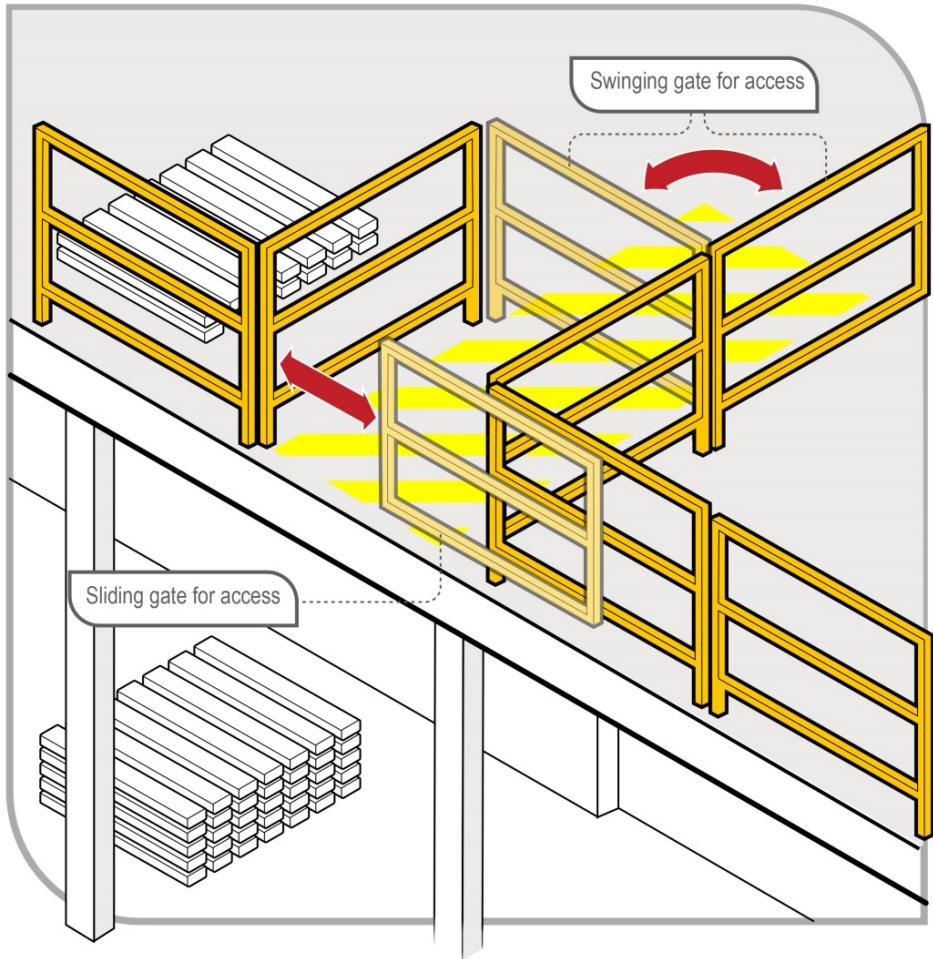 Figure: Mezzanine floor barrier
Figure: Mezzanine floor barrier
 Figure: Guardrails installed on plant for safe access
Figure: Guardrails installed on plant for safe access
Perimeter Safety Screens:
- Mesh attached to structure perimeter
- Catches falling workers and materials
- Used on multi-storey construction
Safety Mesh/Netting:
- Under fragile roof materials
- Below overhead work (catches falling workers/materials)
- Must be installed by competent person
Covers Over Penetrations:
- Secure covers for floor openings, shafts
- Must support weight of person walking on it
- Clearly marked ("HOLE - DO NOT REMOVE COVER")
Guardrails and edge protection are more reliable than fall arrest systems. Use wherever reasonably practicable.
Level 2: Minimize Risk - Work Positioning and Restraint
Fall Restraint Systems: Physically prevents worker from reaching fall edge.
Components:
- Anchorage point (rated, tested, certified)
- Full-body harness
- Lanyard (adjustable, limits travel to prevent reaching edge)
Advantage:
- Prevents fall (worker cannot reach edge)
- No fall arrest forces
Limitation:
- Work area restricted
- May not be practicable for large areas
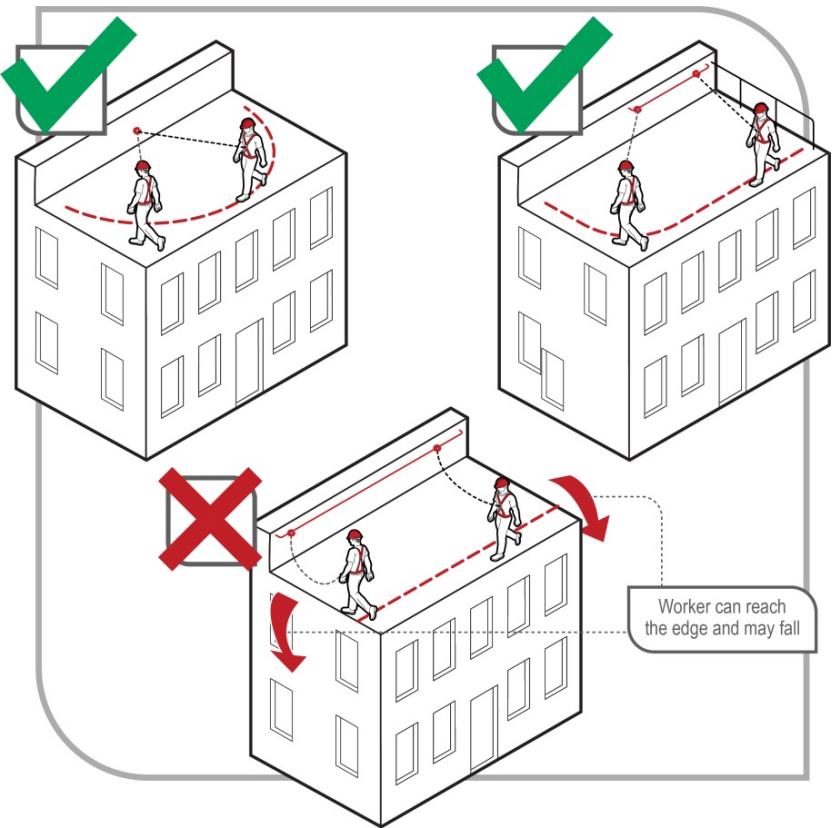 Figure: Restraint technique - prevents reaching the fall edge
Figure: Restraint technique - prevents reaching the fall edge
Example: Worker on roof with harness connected to ridge anchor. Lanyard length prevents reaching eaves.
Level 3: Minimize Risk - Fall Arrest Systems
When Used: Where higher-level controls not reasonably practicable.
Fall arrest stops a fall but does not prevent it. Significant injury risk from fall itself, suspension trauma, and arrest forces.
Components:
1. Anchorage Point:
- Must withstand 15kN (static) or 12kN (if engineered)
- Certified and inspected
- Located to minimize free-fall distance and swing
2. Full-Body Harness:
- AS/NZS 1891.1 compliant
- Correctly fitted to individual
- Dorsal (back) attachment point for fall arrest
3. Connecting Device:
- Shock-absorbing lanyard: Reduces arrest forces
- Self-retracting lifeline (SRL): Arrests falls quickly, minimal free-fall
- Must be compatible with harness and anchorage
4. Rescue Plan:
- Method to rescue fallen worker within 6 minutes
- Suspension trauma can be fatal
- Rescue equipment and trained personnel
Critical Requirements:
- Maximum free-fall distance 2 meters (preferably <1m)
- Minimum clearance below (calculate fall distance + lanyard extension + worker height + safety margin)
- Regular inspection (before each use)
- Training in correct use
- Compatible equipment (not mixing brands without verification)
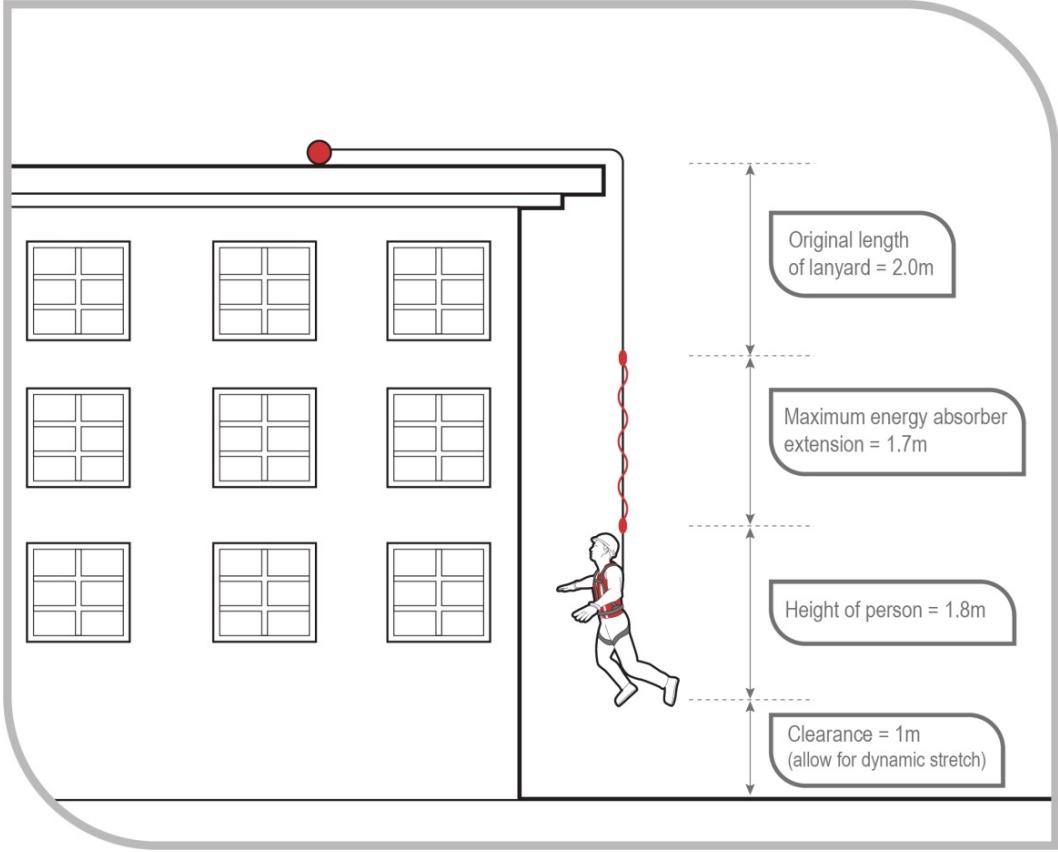 Figure: Calculating total fall distance vs clearance required
Figure: Calculating total fall distance vs clearance required
Example Calculation:
- Worker height: 1.8m
- Free-fall: 1m
- Lanyard extension during arrest: 1.2m
- Safety margin: 1m
- Minimum clearance required: 5m below anchor point
Level 3: Administrative Controls and PPE
Used in conjunction with fall protection systems, not alone:
- Training in fall protection use
- SWMS for work at heights
- Permits for roof access
- Competent supervision
- Weather restrictions (wind, rain, ice)
- PPE (hard hats, safety boots)
Specific Fall Risks and Controls
Roof Work
Fragile Roofs: Materials that won't support person's weight (old corrugated iron, skylight, fiber-cement).
Controls:
- Install walkways/crawl boards (distribute weight)
- Safety mesh under fragile areas
- Edge protection at roof perimeter
- Fall arrest if mesh/rails not practicable
- Never rely on roof material alone
Pitched Roofs:
- Scaffolding with edge protection for installation/maintenance
- Roof brackets and planks (not <30 degrees pitch)
- Fall arrest for steep pitches
- Consider weather (rain, ice makes surfaces slippery)
Ladders
Ladders are for Access, Not Workplaces: Use ladders only for:
- Short duration, low-risk work
- Access to/from another level
Requirements:
- Industrial-rated (not domestic)
- Inspected before use (check rungs, stiles, feet)
- Secured (tied off top and bottom, or footed by second person)
- Correct angle (1:4 ratio - 1m out for every 4m up)
- Extend 1m above landing platform
- Three-point contact (two hands, one foot or two feet, one hand)
- Face ladder when ascending/descending
- Don't carry loads (use tool belt or hoist materials)
When Not to Use Ladders:
- Prolonged work (use scaffold/platform)
- Heavy or awkward loads
- Work requiring two hands
- Work above 2 meters (where scaffold practicable)
Scaffolding
Advantages:
- Large work platform
- Edge protection built-in
- Stable base for materials
- Suitable for prolonged work
Requirements:
- Erected by licensed scaffolder
- Designed for loads (workers + materials)
- Inspected before use and regularly
- Tagged (green = safe, red = unsafe - DO NOT USE)
- Tied to structure (prevents collapse/movement)
- Edge protection (toe boards, mid-rails, top rails)
- Safe access (internal ladder, stairs)
- Level, stable base (base plates, mud sills)
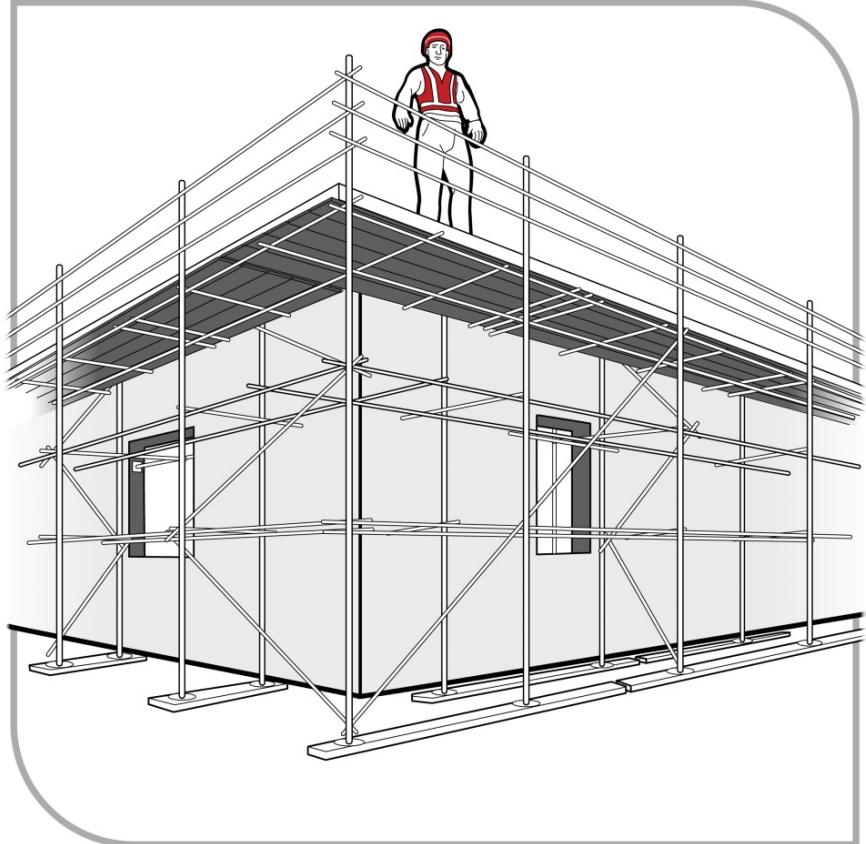 Figure: Perimeter scaffold with guardrails, mid-rails, and toe-boards
Figure: Perimeter scaffold with guardrails, mid-rails, and toe-boards
Inspection:
- Before each shift
- After weather events (strong wind, rain)
- After any modifications
- By competent person
Users Must:
- Check tag before using
- Not modify scaffold
- Not overload
- Not remove edge protection
- Report damage immediately
Elevated Work Platforms (EWP)
Types:
- Scissor lifts (vertical)
- Boom lifts (articulated/telescopic)
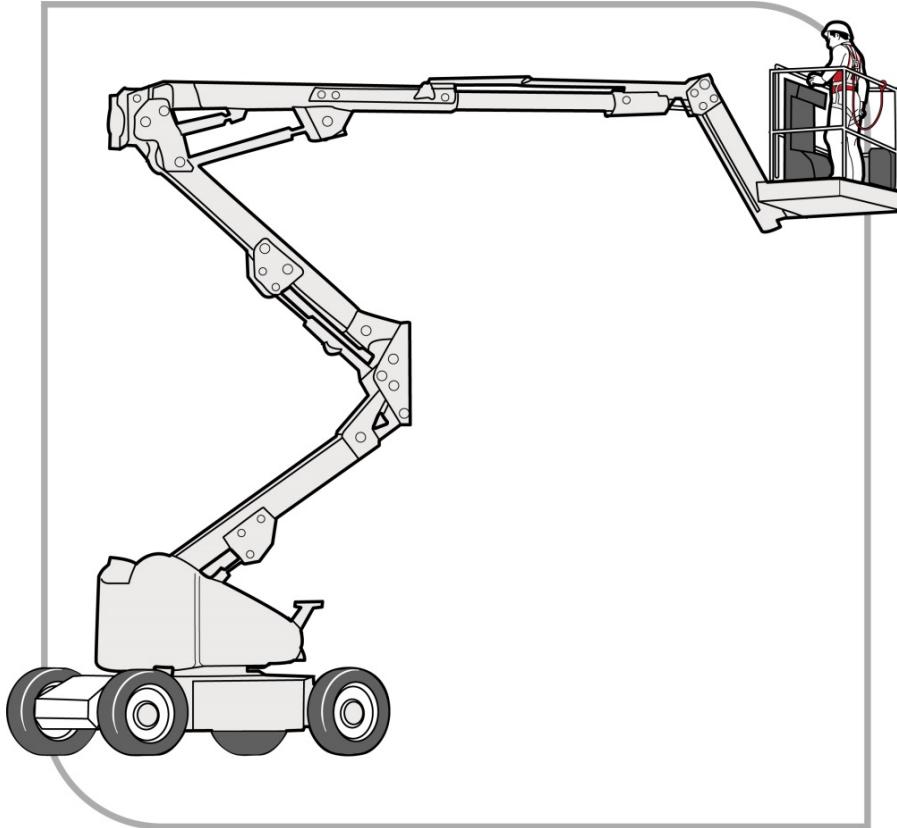 Figure: Boom-type elevating work platform
Figure: Boom-type elevating work platform
Safety Requirements:
- Licensed operator for boom-type (boom length of 11 metres or more)
- Pre-start inspection
- Guardrails on platform (intact, no gaps)
- Harness required for boom-type (anchor to platform, not structure)
- Level, stable ground
- Use outriggers if fitted
- Avoid overhead hazards (powerlines, structures)
- Lower platform when traveling
Fall Protection:
- Scissor lifts: Guardrails (harness generally not required)
- Boom lifts: Guardrails + harness anchored to platform
Excavations
Risk: Falling into excavations (same as falling from height).
Controls:
- Edge protection (barriers, guardrails) around excavation perimeter
- Covers over narrow trenches (must support traffic loads if applicable)
- Warning signs
- Adequate lighting
- Safe access/egress (ladders every 15m)
See Excavation Work for detailed guidance.
Rescue Procedures
Suspension Trauma: Hanging motionless in harness after fall can cause blood to pool in legs, leading to unconsciousness and death within 6-15 minutes.
Rescue Plan Must Include:
- Method to reach and rescue fallen worker
- Equipment (rescue lines, descent devices, EWP, crane)
- Trained rescue personnel
- Communication method (phone, radio)
- Contact emergency services (000)
- First aid and medical treatment
- Target rescue time: <6 minutes
While Awaiting Rescue:
- Conscious worker should move legs (pumping action to maintain blood flow)
- If suspension relief straps available, deploy and stand in them
Practical Construction Example
Scenario: Installing roof sheeting on single-storey warehouse (eaves 5m from ground)
Hazard Identification
- Fall from roof edge (5m fall = fatal)
- Fragile roof lights (not yet installed)
- Weather (wind, rain)
Risk Assessment
- Extreme risk: Fall from 5m onto concrete = likely death or serious injury
Controls Implemented
Engineering (Level 2):
- Perimeter edge protection installed before roof work starts (guardrails on all edges)
- Safety mesh installed under areas where roof lights will be fitted
- Scaffolding with edge protection on one side for material delivery and safe access
Administrative:
- SWMS prepared and reviewed with workers
- Only competent roofers permitted on roof
- Work stopped if wind >30 km/h or rain
- Exclusion zone on ground (5m from building perimeter)
PPE:
- Hard hats (falling objects from edge)
- Safety boots, gloves
- Fall arrest harness (backup - edge protection is primary control)
Result
Roof installed safely. Edge protection prevented any falls. Mesh provided backup protection at roof light penetrations.